Category: investments
-

What is the risk-free rate?
in investmentsThe risk-free rate is the rate of return earned on a risk-free asset. While returns on risky assets such as stocks are uncertain, the key distinction of the risk-free rate of return is that we know its exact value at the time of investment. For example, we may expect a stock to yield 8% over…
-

Return volatility formula and calculator
We start this lesson by discussing what is meant by (stock) return volatility. Then, we explain the return volatility formula. Finally, a simple return volatility calculator is provided for your convenience. What is (stock) return volatility? Imagine an investor who bought shares of a stock three years ago. According to the investor’s calculations, her annual…
-

Arithmetic average return calculator and formula
In this lesson, we introduce a simple yet really useful measure of investment performance. In particular, we discuss the arithmetic average return formula and provide a practical arithmetic average return calculator. It is really important for investors to be able to accurately assess the performance of their investments. In that sense, arithmetic average (or mean)…
-

Geometric average return calculator and formula
In this post, we explain the geometric average return formula using numerical examples and discuss how it differs from the arithmetic average return. We provide a practical geometric average return calculator as well. Geometric average return formula The geometric average return formula can be written as follows: While the formula looks complicated at first sight,…
-

What is risk pooling?
in investmentsRisk pooling is an important concept that is particularly relevant for areas such as finance, insurance, supply chain management, and healthcare. In this post, we offer a definition of risk pooling, provide examples, and discuss the relevance of risk pooling in different areas. We draw a distinction between risk pooling and risk sharing as well.…
-

Risk aversion coefficient – meaning and formula
When we discussed investors’ risk preferences, we distinguished between risk-averse, risk-neutral, and risk-seeking behavior. We also explained that risk-averse investors expect compensation for bearing risk, which is called a risk premium. But, how do measure risk aversion? The answer is the risk aversion coefficient. It quantifies the degree to which an individual dislikes risk. In…
-
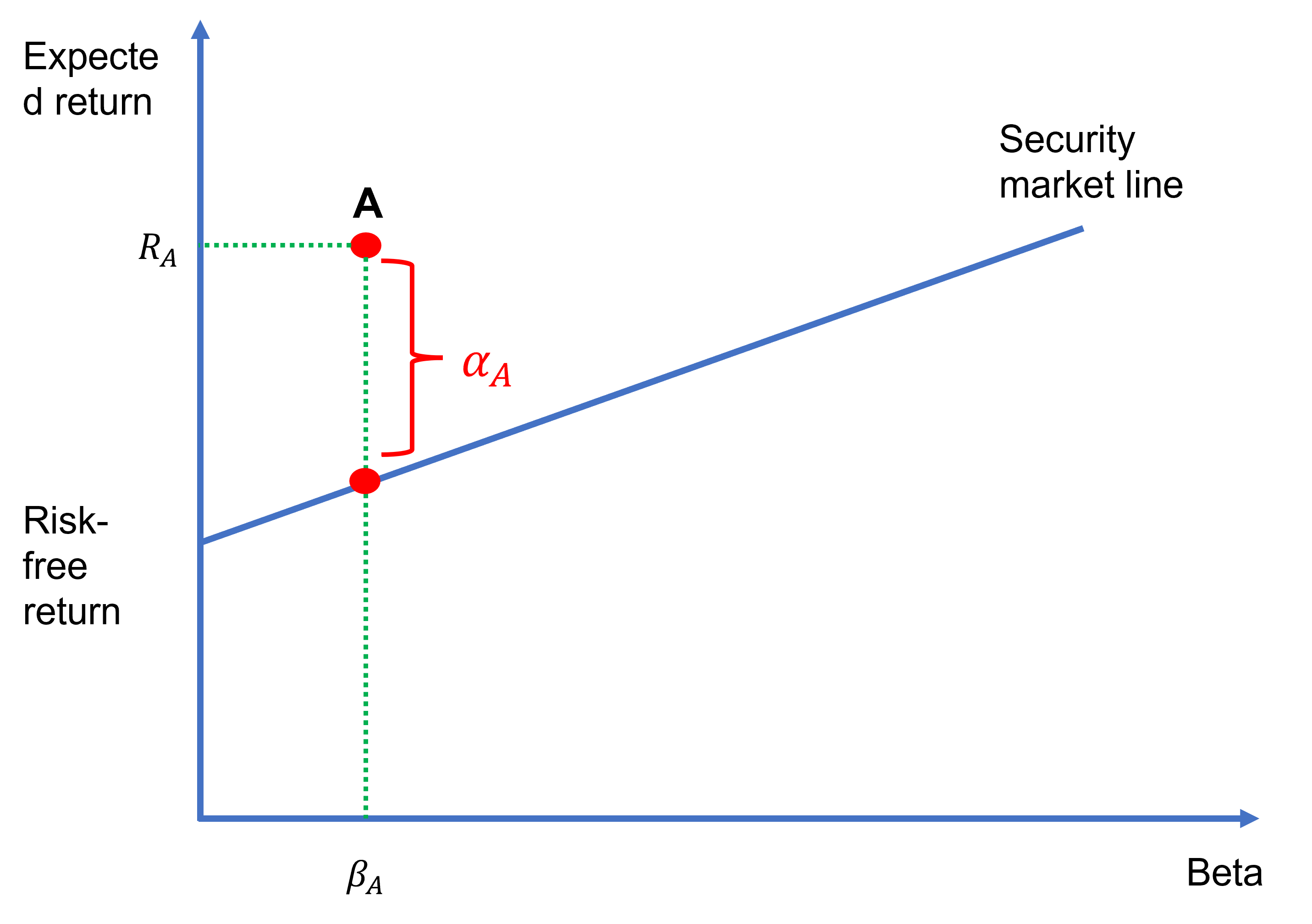
Jensen’s alpha formula and calculator
Jensen’s alpha is a popular performance evaluation metric, which was developed by the American financial economist Michael Jensen in the late 60s. It is a risk-adjusted performance measure (other examples include the Sharpe ratio and Treynor ratio) and is theoretically linked to the capital asset pricing model (or the CAPM). Jensen’s alpha formula We can…
-

Investments quiz – Test your knowledge!
in investmentsThis investments quiz aims to test your knowledge of the material covered in our free investments course. The quiz is a multiple-choice test. It consists of three sections: The answers and solutions are provided at the bottom of this page. Section A: Return calculations 1. You buy a single share of a stock for $10.…
-
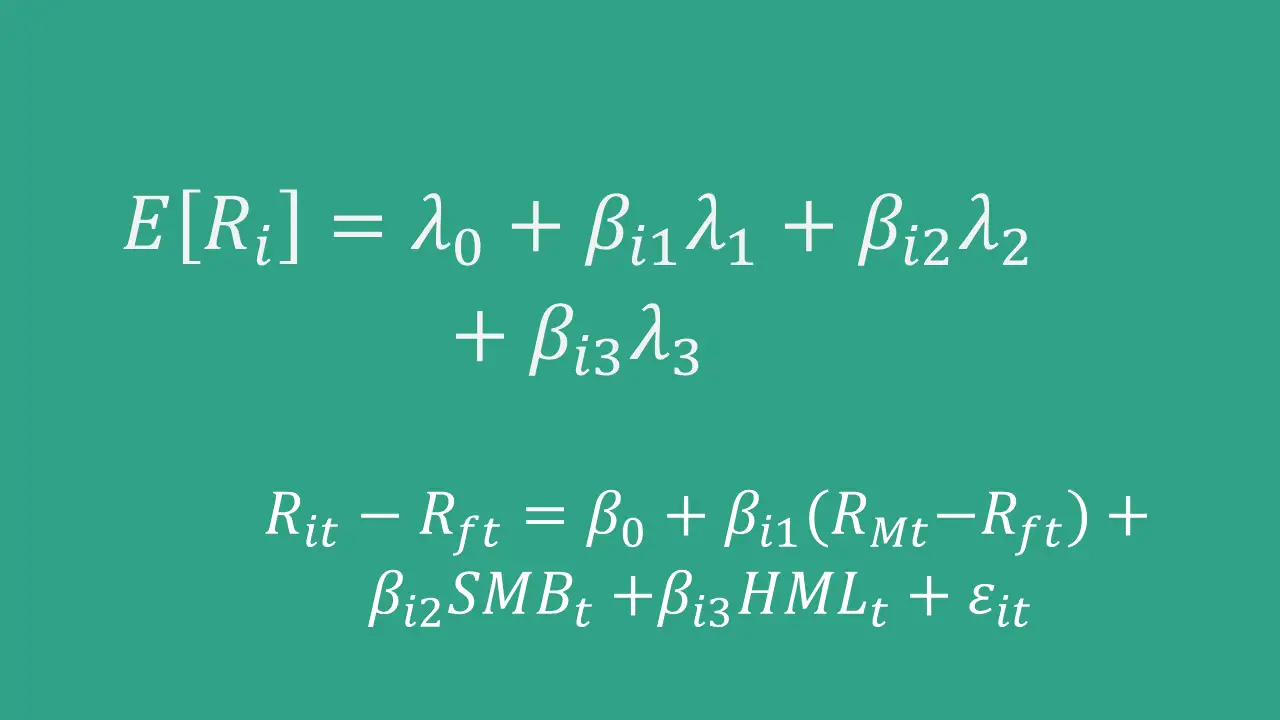
Arbitrage pricing theory (APT)
Arbitrage pricing theory (APT) is an asset pricing model developed by the American economist Stephen Ross in the mid-1970s. While the capital asset pricing model (CAPM) posits a single systematic risk factor, which is the market risk, arbitrage pricing theory accommodates multiple risk factors. As such, APT has been the driving force behind the growth of multi-factor…
-
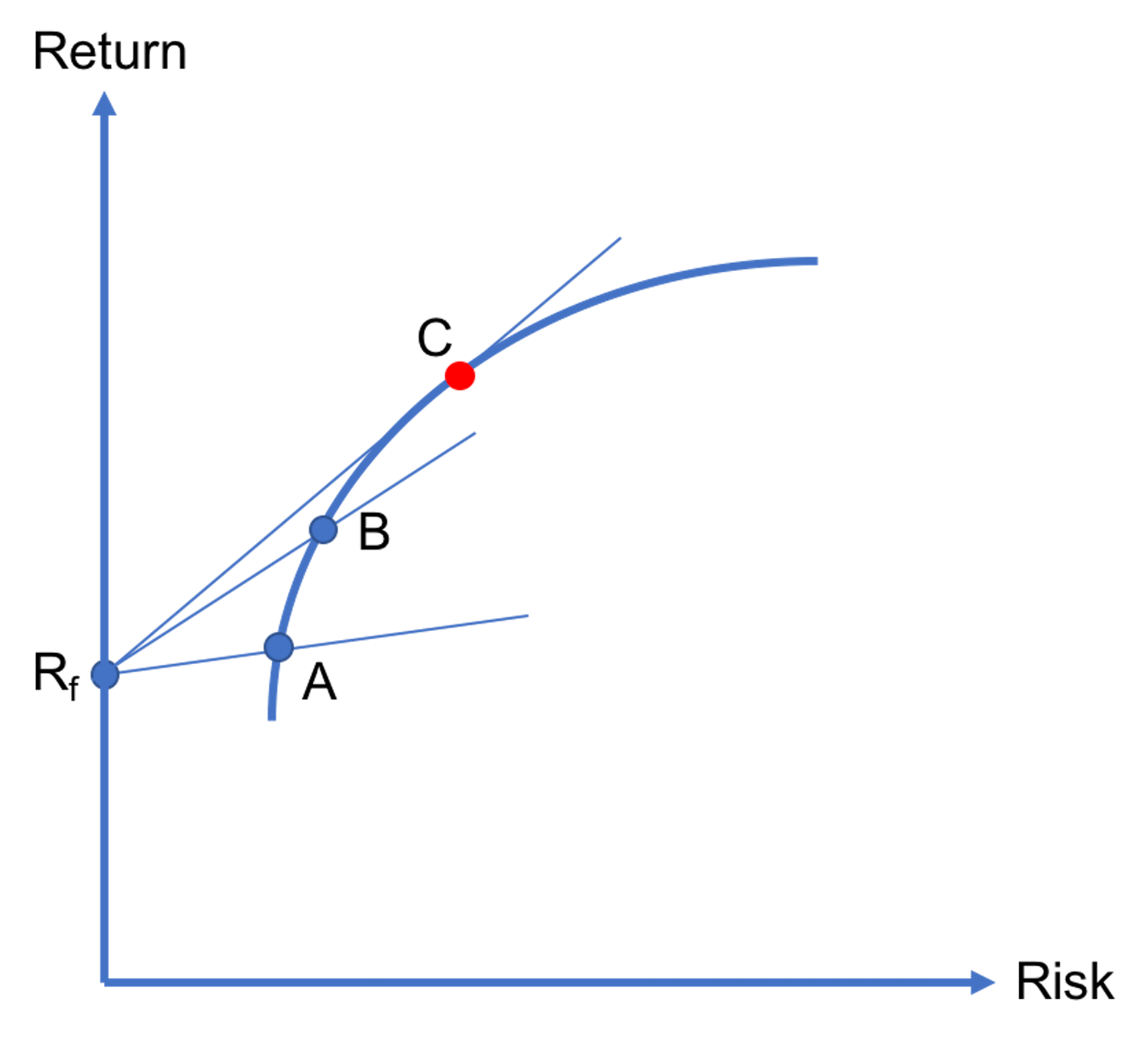
Optimal risky portfolio
In previous lessons, we explained that when there is no risk-free asset in an economy, investors should invest in one of the efficient portfolios that lie on the efficient frontier based on their risk tolerances. But, if a risk-free asset exists, then there is a unique efficient portfolio that all investors should invest in. In…
