Category: portfolio theory
-

Portfolio risk calculator and formula
We often say that risk and return are two sides of the same coin. So, when assessing the performance of a portfolio, we need to consider its risk as well as its return. In the previous lesson, we focused on portfolio return. Now, we turn our attention to portfolio risk. Portfolio risk calculator You can…
-
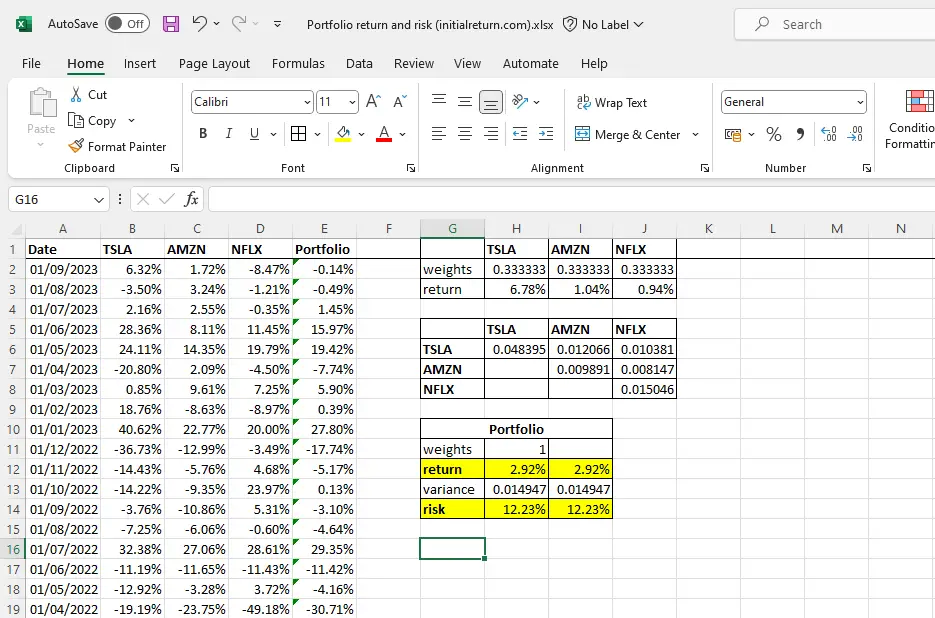
How to calculate portfolio risk and return in Excel
In this tutorial, we’ll teach you how to calculate portfolio risk and return in Excel. We’ll focus on an example where we construct a portfolio of the following three stocks: Tesla (TSLA), Amazon (AMZN), and Netflix (NFLX). If you’re unfamiliar with the formulas for portfolio return and portfolio risk, we’d recommend you check the following…
-
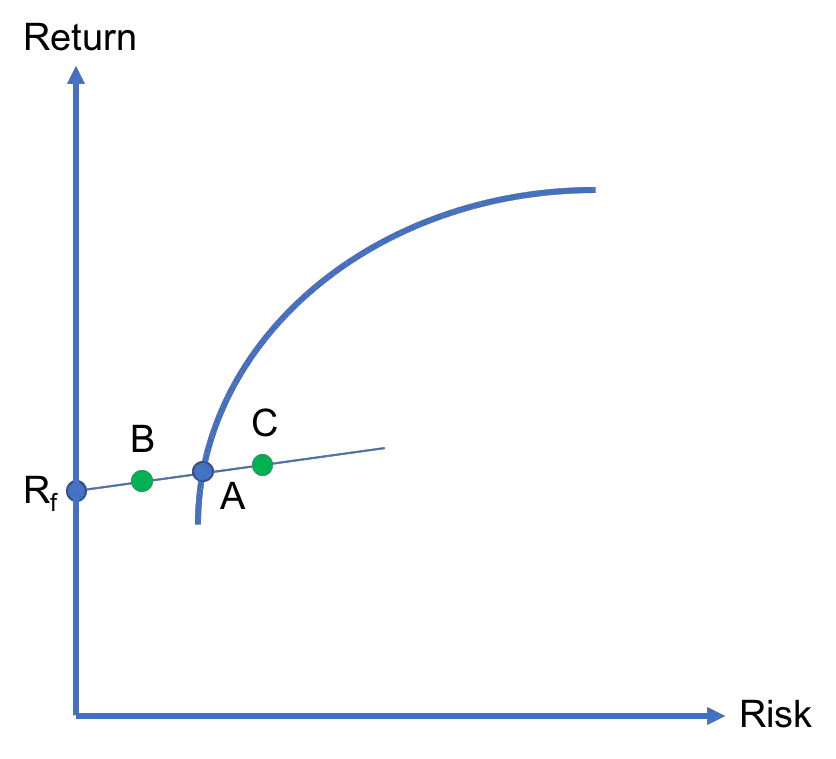
Capital allocation line
When a risk-free asset exists in an economy, investors can add that asset to their portfolios if they wish so. In the risk-return space, the combination of the risk-free asset and any risky asset is a straight line. This line is called the capital allocation line as it shows how an investor’s capital is allocated…
-

Market portfolio
We have so far learned how to calculate the risk and return of portfolios and how to trace an efficient frontier through mean-variance optimization. It is now time to introduce a special portfolio that will play a significant role when we discuss the CAPM: The market portfolio. What is the market portfolio? The market portfolio is the…
-

Minimum variance portfolio
In this lesson, we explain what is meant by the minimum variance portfolio (MVP), derive its formula for the two-asset case, and provide an online calculator as well. You can also check out our video tutorial to learn how to find the position of the MVP on the efficient frontier using Excel’s solver tool. And,…
-
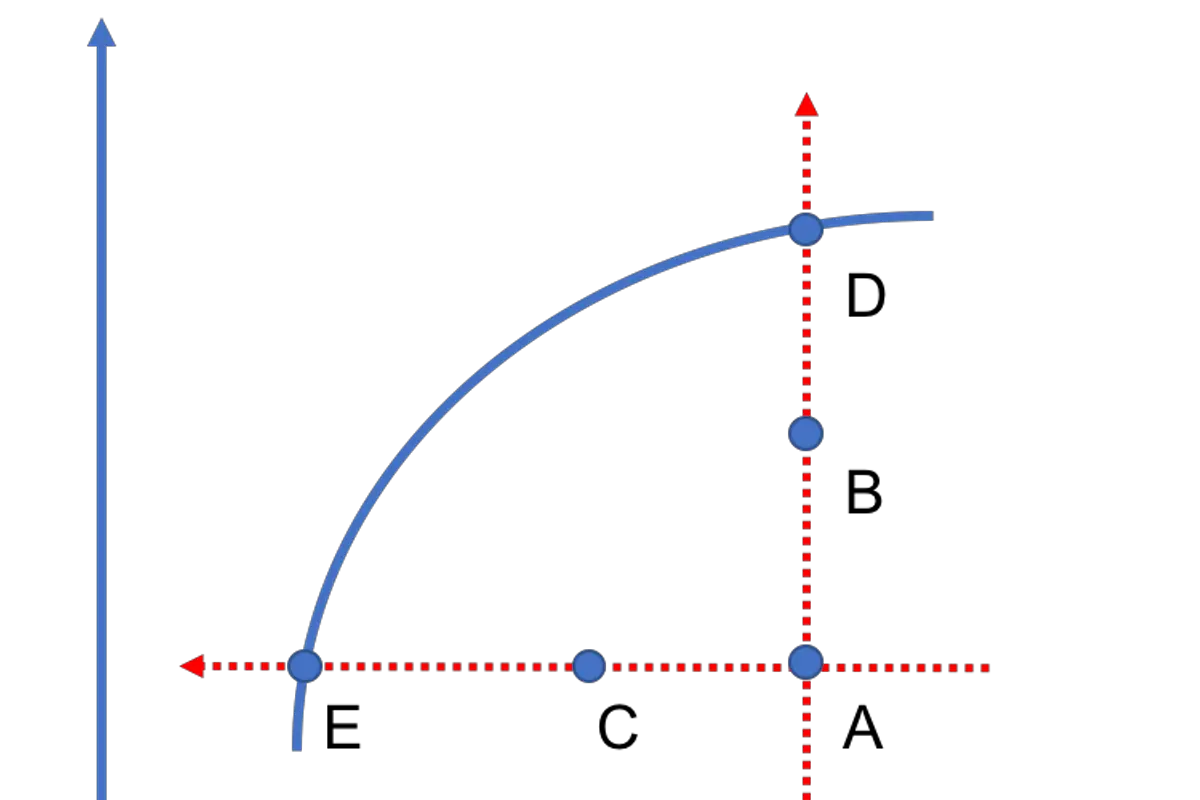
Efficient frontier calculator
In modern portfolio theory, the efficient frontier represents the collection of all efficient portfolios within a market. Efficient portfolios offer the best risk-return tradeoff and, as such, are superior to inefficient portfolios, which are suboptimal. In this lesson, we explain how investors can trace the efficient frontier using mean-variance optimization (the topic of the previous…
-
Mean-variance optimization
According to modern portfolio theory, investors are concerned about the “mean” and “variance” of asset returns, where the former captures the “centrality” and the latter the “spread” (or “riskiness”) of potential returns. As such, investors engage in mean-variance optimization. That is, they seek the portfolios that offer the best tradeoff between risk and return. In…
-

Idiosyncratic risk
Idiosyncratic risk is the type of risk that affects either a single security such as a stock or a small group of securities. This is in contrast to systematic risk, which affects all risky securities in a particular market. The word “idiosyncratic” is not commonly used in daily language. ln fact, idiosyncratic risk is often…
-

What is the risk-free rate?
The risk-free rate is the rate of return earned on a risk-free asset. While returns on risky assets such as stocks are uncertain, the key distinction of the risk-free rate of return is that we know its exact value at the time of investment. For example, we may expect a stock to yield 8% over…
-
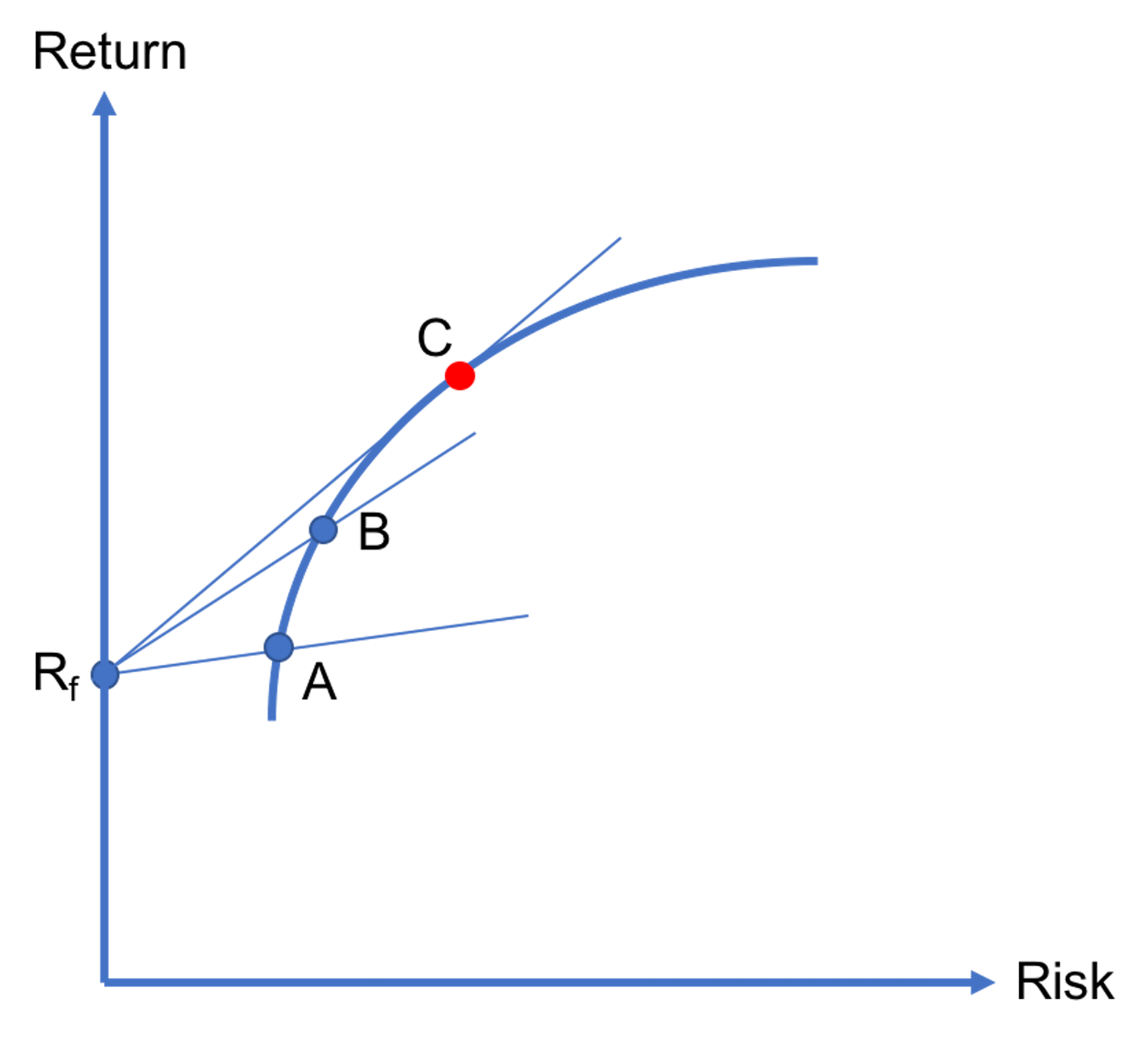
Optimal risky portfolio
In previous lessons, we explained that when there is no risk-free asset in an economy, investors should invest in one of the portfolios that lie on the efficient frontier based on their risk tolerances. But, if a risk-free asset exists, then there is a unique portfolio that all investors should invest in. In particular, the…
